Here We produce 0 Carbon FootprintSustainabilityNatural Life For The Nature
We're not just building; we're crafting a symphony of insulation. By seamlessly integrating insulating materials within its layers, CLT emerges as a masterpiece of warmth and energy efficiency, redefining the way we experience comfort within architectural spaces.

The Best Berry® Way Of CLT
We the Berry Group, are renowned for our commitment to quality and innovation in producing top-notch CLT. We utilize sustainable timber, cutting-edge technology, and a skilled team to ensure every product meets the highest standards.
With our rigorous quality control and a strong focus on environmental sustainability, We have earned a reputation for delivering exceptional CLT solutions. This makes us a trusted choice for builders and architects seeking top-quality construction materials.
One Product For All
Offers limitless possibilities for construction. Its exceptional structural and insulating qualities make it a versatile choice for various applications.
In wall construction, CLT efficiently handles vertical forces, while its excellent insulation properties contribute to energy efficiency and a comfortable indoor environment. For ceilings and roofs, CLT is ideal for spanning large distances with low profiles, making it a practical choice for structural needs. Prefabricated components also ensure swift installation."
Wall
Ceiling
Dimensions
| Panel Thickness, mm | Number of Layer | Lamellae thickness, mm | ||||||||
| 60 | 3 | 20 | 20 | 20 | ||||||
| 80 | 3 | 20 | 40 | 20 | ||||||
| 90 | 3 | 30 | 30 | 30 | ||||||
| 100 | 3 | 40 | 20 | 40 | ||||||
| 120 | 3 | 40 | 40 | 40 | ||||||
| 140 | 5 | 40 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 40 | ||||
| 160 | 5 | 40 | 20 | 40 | 20 | 40 | ||||
| 180 | 5 | 40 | 30 | 40 | 30 | 40 | ||||
| 200 | 5 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | ||||
| 220 | 7 | 40 | 20 | 40 | 20 | 40 | 20 | 40 | ||
| 240 | 7 | 40 | 40 | 20 | 40 | 20 | 40 | 40 | ||
| 260 | 7 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 20 | 40 | 40 | 40 | ||
| 280 | 7 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | ||
| 300 | 7 | 50 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 50 | ||
| 320 | 7 | 50 | 50 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 50 | 50 | ||
| 340 | 7 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 40 | 50 | 50 | 50 | ||
| 360 | 9 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| 380 | 9 | 50 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 50 |
| 400 | 9 | 50 | 50 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 50 | 50 |
| 420 | 9 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
Technical Specifications
Areas Of Use
- Residential Construction
- Commercial Buildings
- Educational Facilities
- Industrial Facilities
- Cultural and Recreational Facilities
- Healthcare Facilities
- Multi-Story Buildings
- Residential Renovations and Extensions
- Prefabricated Homes
- Interior Design
- Bridges and Pedestrian Walkways
- Temporary Structures

| Application | Structural elements for walls, floors and roofs |
| Maximum element dimensions | Length: 16 m / Width: 3.45 m / Thickness: 0.35 m |
| Invoiced widths | 2.25 m / 2.45 m / 2.75 m / 2.95 m / 3.25 m* / 3.45 m* |
| *Please contact your local sales representative for more information regarding the larger dimensions | |
| Panel lay-up | 3, 5, 7 or more layers depending on structural design requirements |
| Wood species | Spruce (silver fir ,larch and pine on request) |
| Strength class | C24 according to EN 338, maximum 10% C16 permitted (other strength class compare with ETA 14/0349) |
| Moisture content | 12% +/-2% on delivery |
| Adhesive | Formaldehyde-free for finger jointing and surface bonding, |
| approved for load-bearing and non-load-bearing components indoors and outdoors according to EN 15425; Formaldehyde-free EPI adhesive for narrow side bonding | |
| Surface quality | Non-visual quality (NVI), Industrial visual quality (IVI) and Visual quality (VI); the surfaces are always sanded on both faces |
| Weight | For determining transport weight: approx. 470 kg/m³ |
| Fire rating | In accordance with Commission Decision 2003/43/EC: |
| •Timber components (apart from floors) е Euroclass D-s2, d0 | |
| •Floors е Euroclass Dfl-s1 | |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.12 W/(mK) |
| Air tightness | CLT panels are made up of at least three layers of single-layer panels and are therefore extremely air-tight. The air-tightness of a 3-layer CLT panel was tested according to EN 12 114 |
| Service class | Service class 1 and 2 according to EN 1995-1-1 |

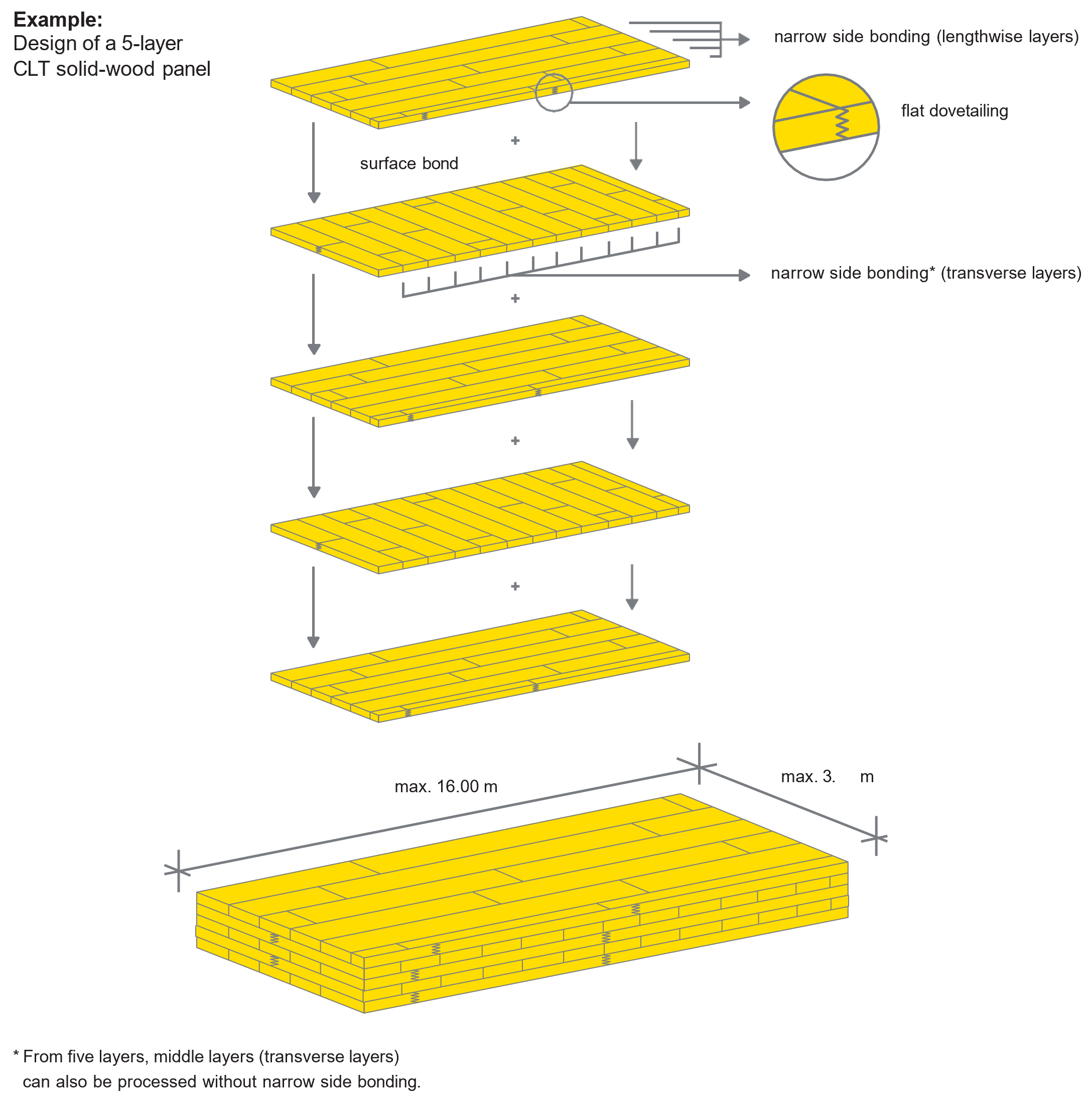
Panel design
CLT solid wood panels are made up of at least three layers of bonded single- layer panels arranged at right angles to one another. From five layers, CLT can also include middle layers (transverse layers) without narrow side bonding. It can currently be produced with dimensions of up to 3.45 × 16.0 m.
| CLT surface quality | |||
| Surface quality appearance with respect to product characteristics | |||
| Characteristics | VI | IVI | NVI |
| Surface finish | sanded | sanded | ≤ 10 % of the surface may not be sanded |
| Timber species | one single species | one single species | addition of other timber species allowed |
| Moisture content | ≤ 11 % | ≤ 15 % | ≤ 15 % |
| Narrow side bonding | occasional open joints permitted | occasional open joints permitted | occasional open joints permitted |
| ≤ 1 mm | ≤ 2 mm | ≤ 3 mm | |
| Discolouration | slight discolouration permitted | slight discolouration permitted | permitted |
| ≤ 1 % | ≤ 3 % | ||
| Knots — sound | permitted | permitted | permitted |
| Knots — black | occasional occurences permitted | permitted | permitted |
| ≤ 15 mm Ø | ≤ 30 mm Ø | ||
| Loose knots, knot holes | occasional occurences permitted | permitted | permitted |
| ≤ 10 mm Ø | ≤ 20 mm Ø | ||
| Resin pockets | occasional occurences permitted | occasional occurences permitted | permitted |
| ≤ 5 x 50 mm | ≤ 10 x 90 mm | ||
| Bark ingrowths | occasional occurences permitted | occasional occurences permitted | permitted |
| Rough edges / wane | not permitted | not permitted | permitted ≤ 20 x 500 mm |
| Hartwood pith | occasional occurences permitted | permitted | permitted |
| ≤ 400 mm length | |||
| Cracks and gaps between lamella | occasional occurences permitted | occasional occurences permitted | occasional occurences permitted |
| (at reference moisture of 11%) | ≤ 1 mm | ≤ 2 mm | ≤ 3 mm |
| Boreholes from inactive insect attack | not permitted | not permitted | occasional occurences permitted |
| Quality of surface finish | occasional small defects permitted | occasional defects permitted | occasional defects permitted |
| Quality of end grain | occasional small defects permitted | occasional defects permitted | occasional defects permitted |
| Surface retreatment (plugs, fillers, strips, etc.) | permitted | permitted | permitted |
| Chamfer on L-panels in grain direction | yes | yes | no |
| Sanding scratches / sanding directions | Sanding marks on L-panels run in grain direction, on C-panels across grain direction. | ||
| CNC cutting on visual quality (VI) surface | CNC cutting on visual quality (VI) surface will be carried out exclusively with | ||
| milling and cutting tools that cause no soiling through chain oil. | |||
| Crack formations | Crack formations and open joints caused by swelling and shrinking due to later equilibrium moisture in normal use status is wood specific and cannot be prevented. | ||
| Validity | The quality requirements to the surfaces listed above are valid: | ||
| •on delivery • for top and bottom surfaces only | |||
| All end grains / edges are to be considered as NVI quality. | |||

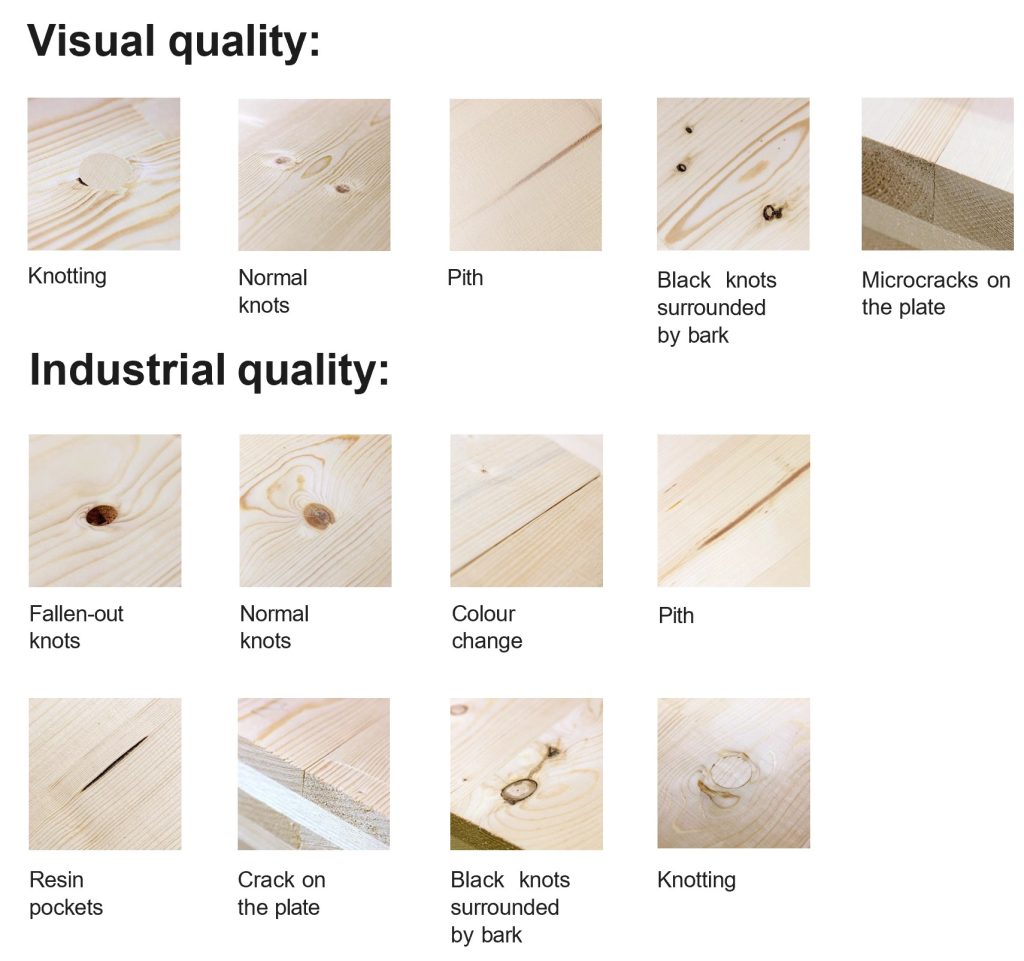
Permissible defects of wood
Depending on the segment of application and the requirements of the client, the Berry CLT plant can offer the following types of surface quality: visual and industrial. They have qualitative differences:
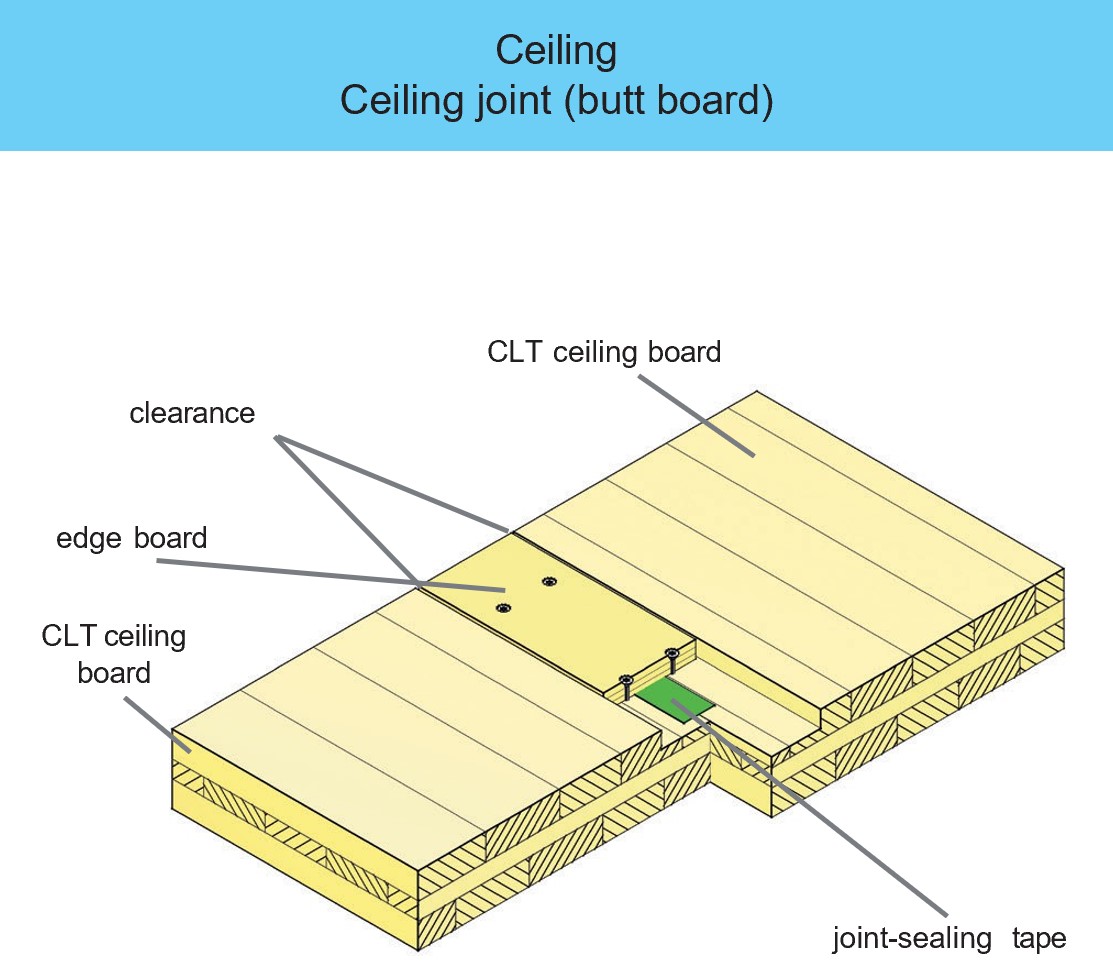
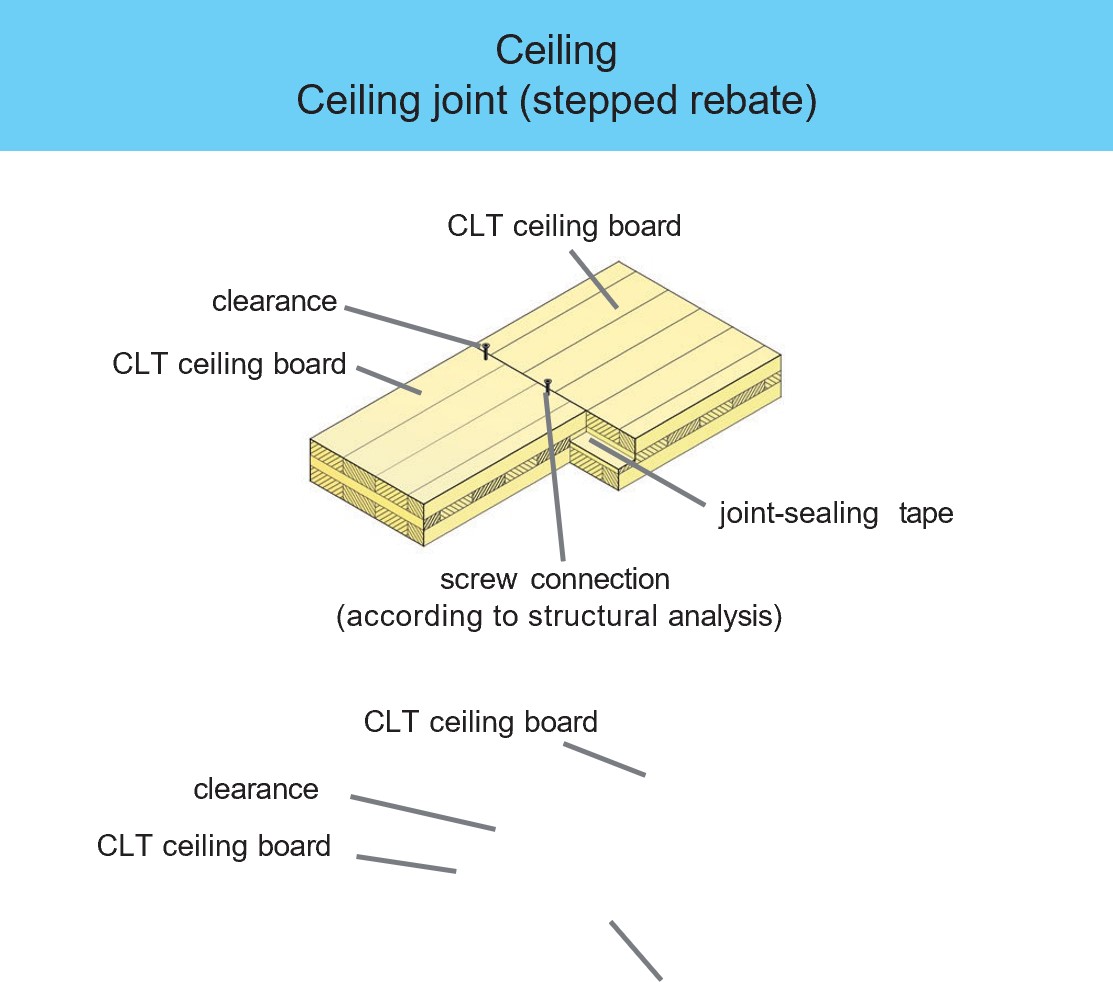
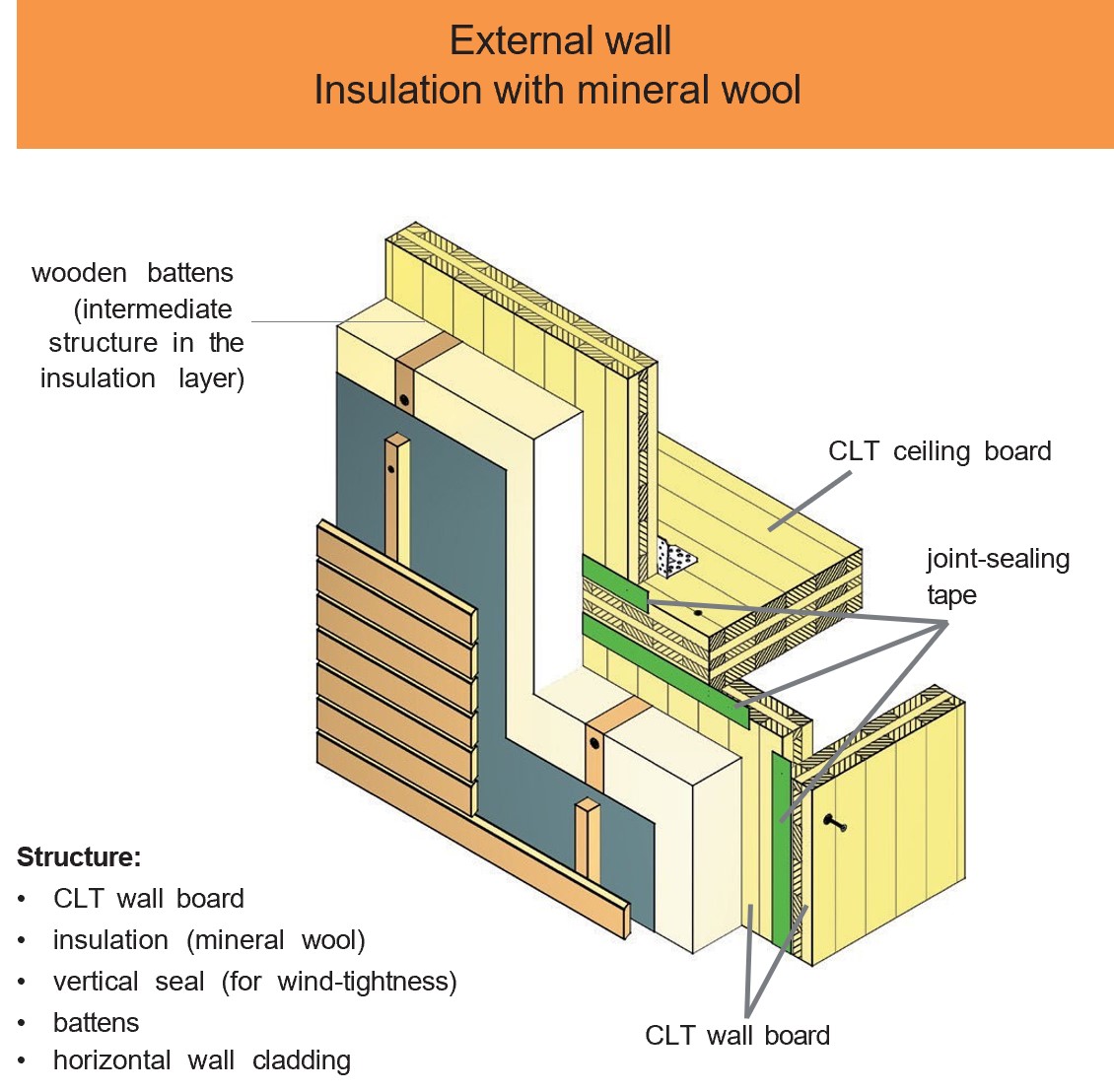
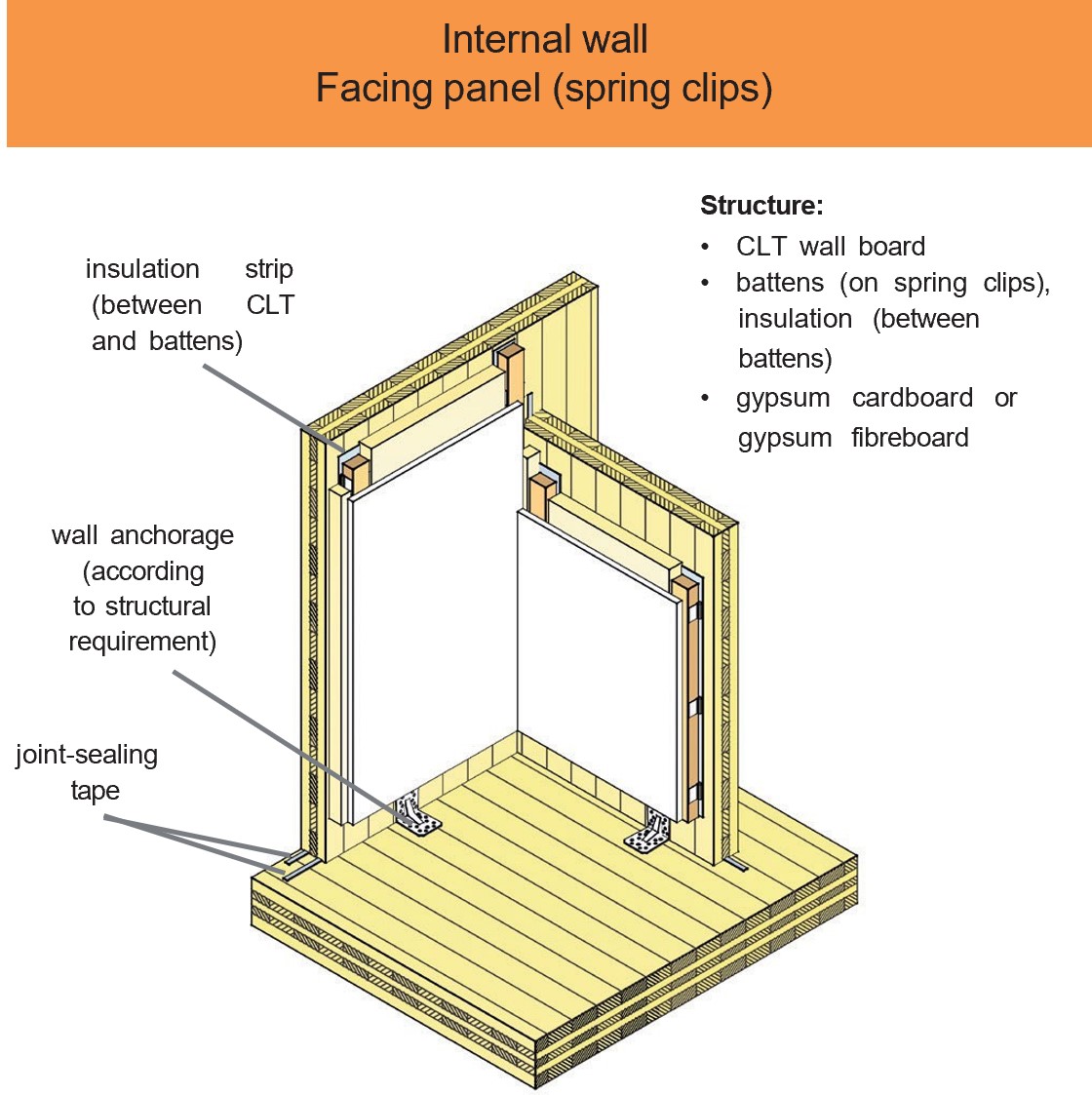
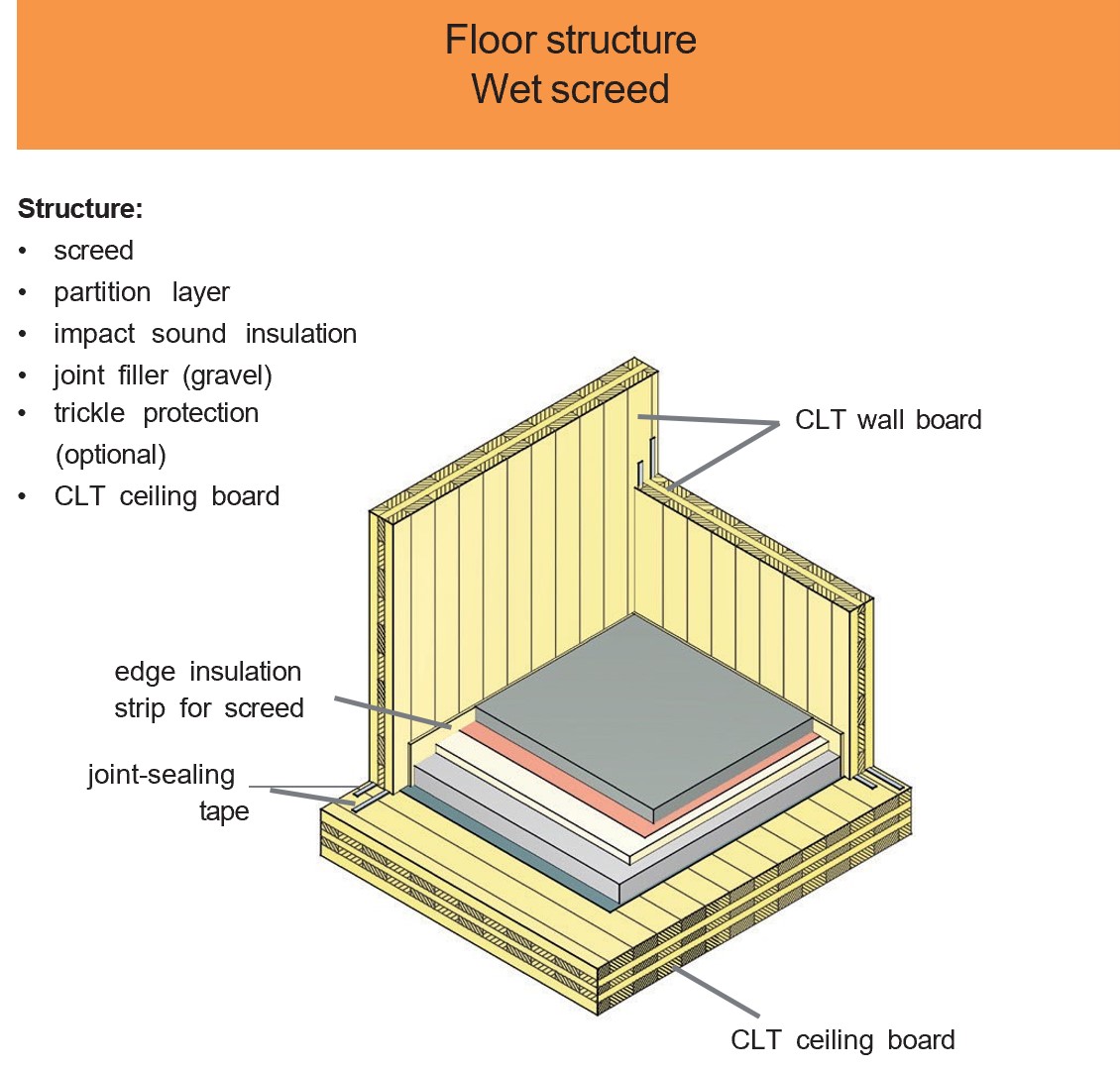
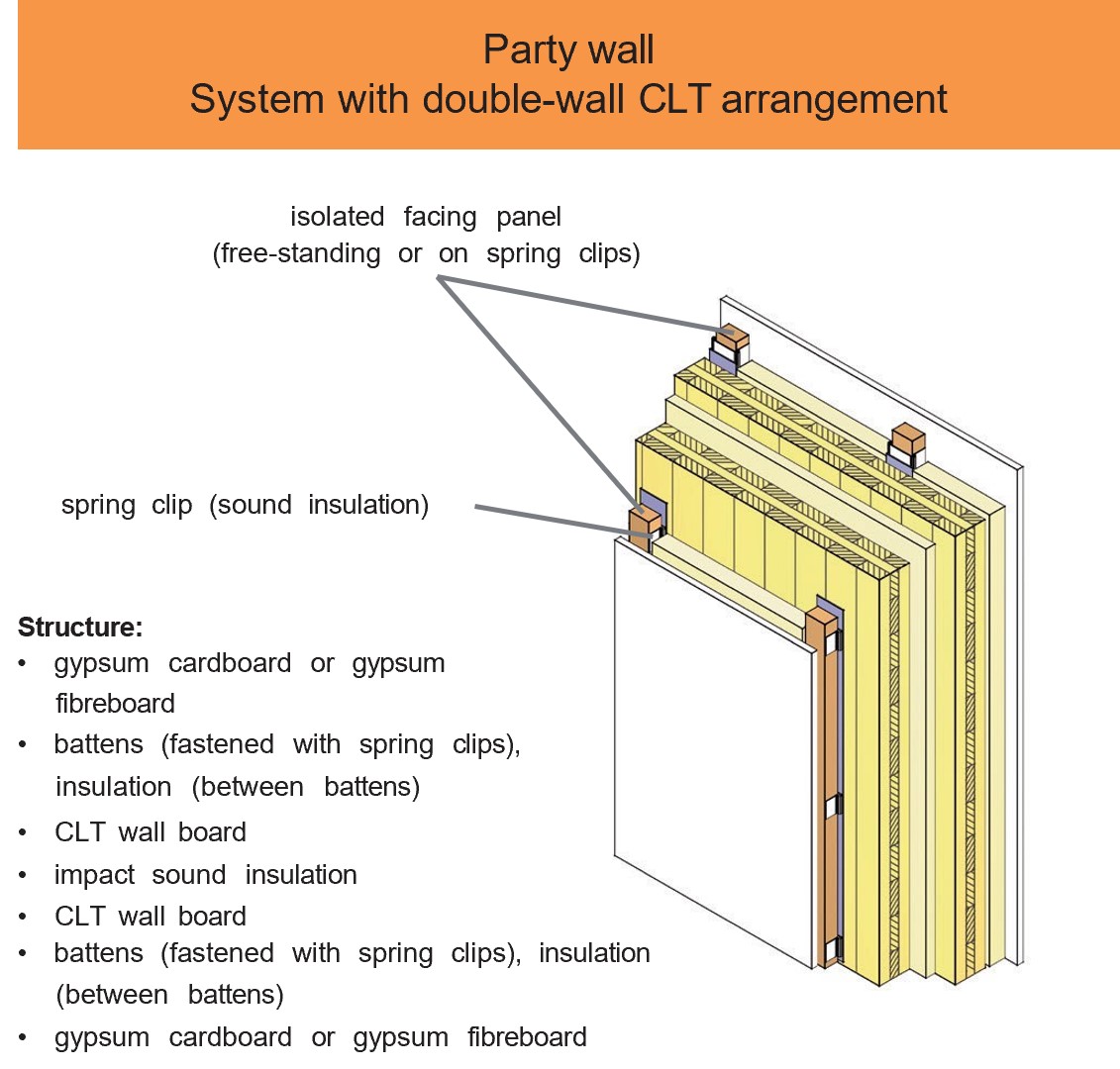
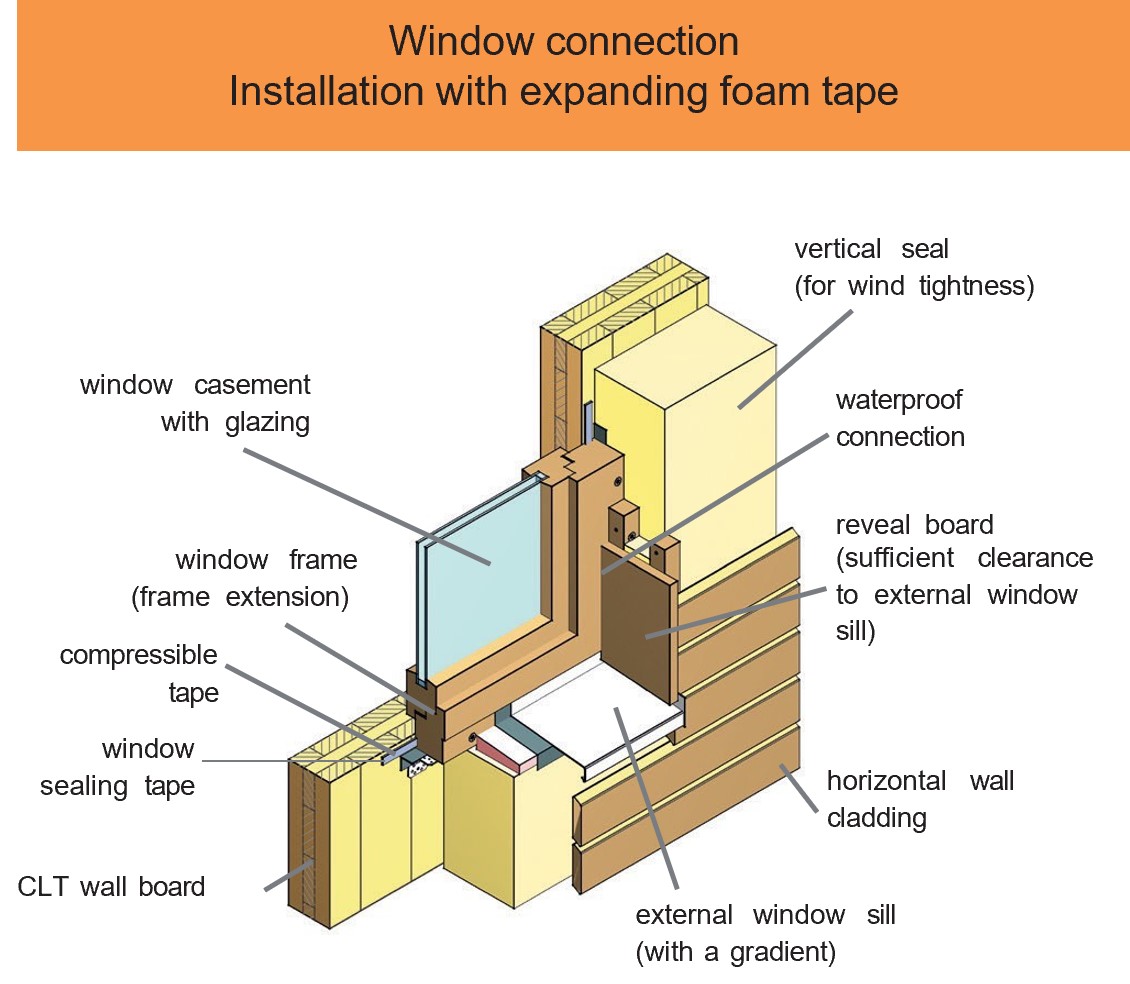
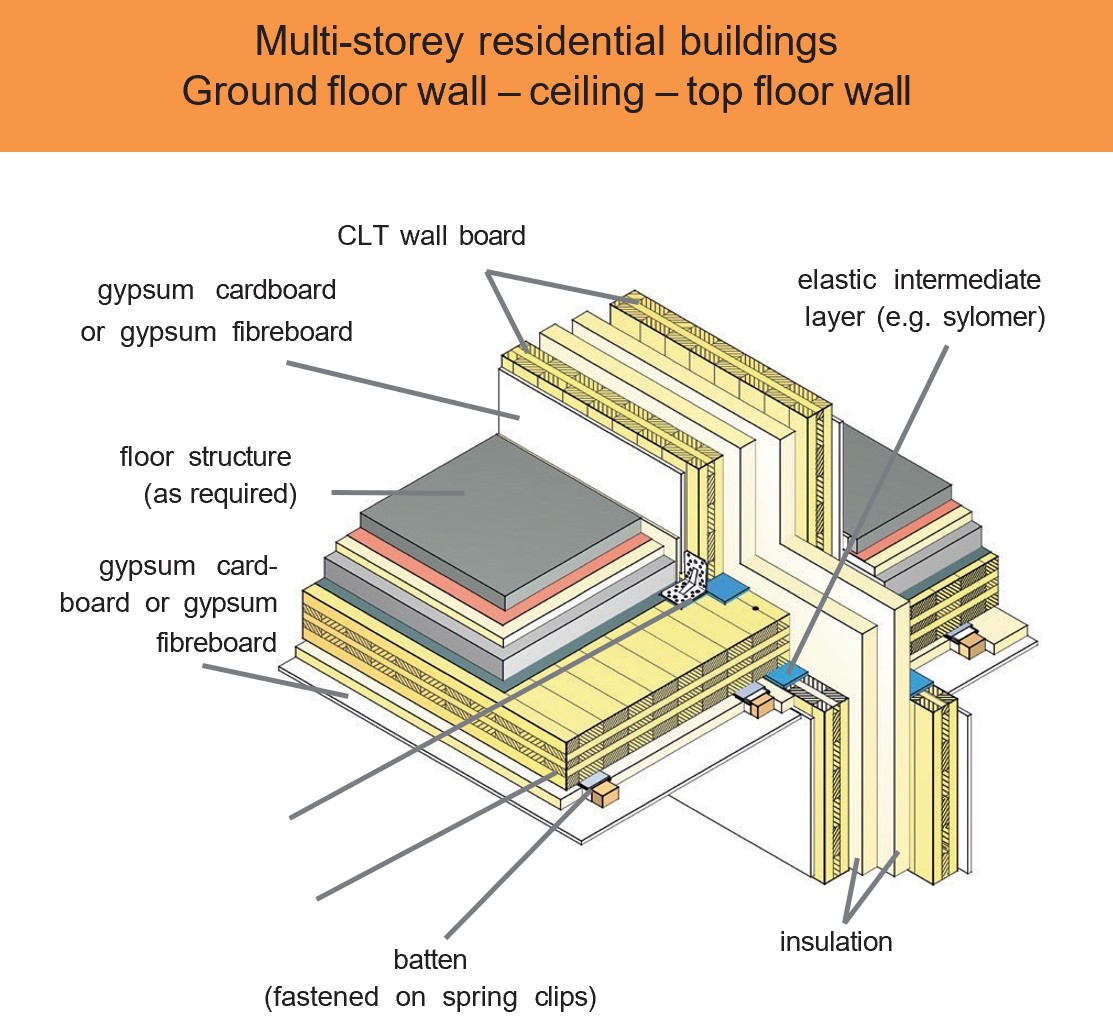
Examples of design details and component designs
CLT elements have a wide range of applications. For example, when used on external, internal and partition walls, due to their structure which consists of bonded boards arranged at right angles to one another, they assume both a load-bearing and a bracing function in the building.
The high level of prefabrication and related short assembly times are a major advantage, especially when CLT panels are used as
roof elements, as buildings can be rendered rain-proof in short time scales. Thanks to CLT, roofs and ceilings can be economically designed with standard span lengths,
and building requirements can be fully satisfied. With the right choice of structural components this can be easily achieved and, at the same time, CLT can be combined with virtually any type of construction material.
CLT – innovative construction technologies
CLT structures are widely used in construction thanks to
- Low weight of structures, high stiffness due to layered design, and ability to withstand heavy loads without shrinkage or deformation
- wide architectural applications, quick assembly on site, possible combination with other building materials
- High energy efficiency and fire resistance characteristics
- modern design solutions that allow building safe and durable structures; CLT can be used in the construction of buildings in seismic zones

- Waste-free full-cycle production process.
- Construction process leaves minimum waste and construction debris.
- Production of CLT structures uses an environmentally friendly adhesive without formaldehyde.
- Temperature inside CLT buildings can be maintained using as little as one third of the energy needed for heating or cooling of an individual house.
Benefits of using CLT panels
in the construction of buildings and structures
|
|
Thermal insulation with CLT
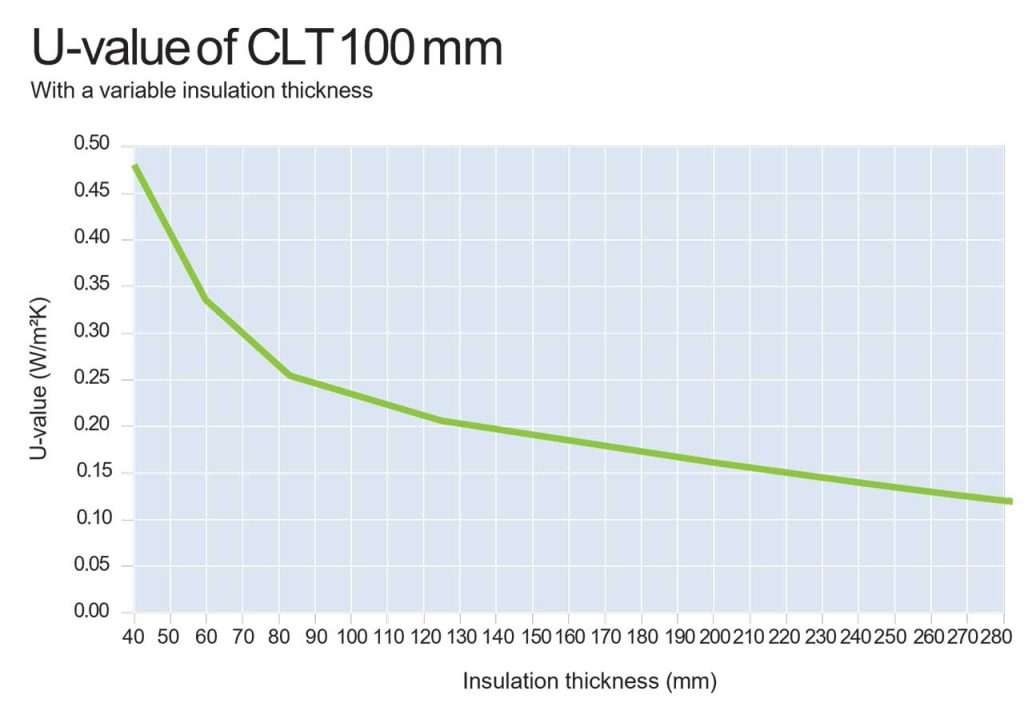
The thermal performance of a component is determined by its U-value or rate of transfer of heat (also known as thermal transmittance). The location in the building and the structure, thermal conductivity and dimensions of the individual materials contained must be known in order to calculate this value. The thermal conductivity of wood is essentially determined by its bulk density and wood moisture content and can be calculated for CLT with a value of λ = 0.12 W/mK.
The following illustration shows a graph on which the U-values of insulated CLT panels with a thickness of 100 mm are plotted depending on the thickness of the insulation material (thermal conductivity group WLG 040).
¹) Quantity of heat which must be supplied to the building during the course of one year in order to keep a minimum room temperature.
²) Quantity of heat which must be evacuated from the building during the course of one year in order not to exceed a maximum room temperature.
Thermal insulation factors and principles in the winter
|
|